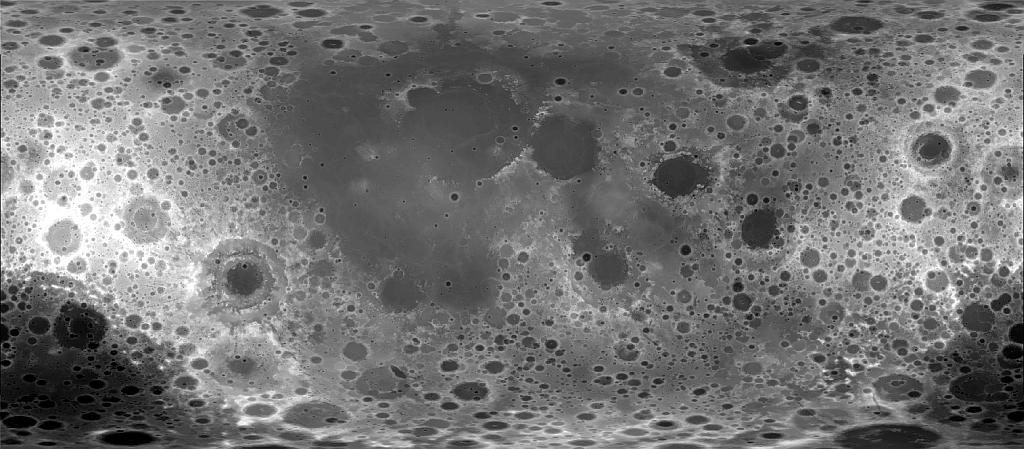
Moon LROC WAC DTM GLD100 118m
- Primary Authors
- LROC Team
- Originators
- F. Scholten, J. Oberst, K.-D. Matz, T. Roatsch, M. Wählisch, E. J. Speyerer, M. S. Robinson
- Publisher
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Publication Date
- 2013-08-01
- Abstract
- Product Information: This product represents a near-global lunar topography from stereo image data acquired by the Wide-angle Camera (WAC) of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) system (Robinson et al., 2010). From polar orbit tracks, the LROC WAC provides image data with a mean ground resolution at nadir of 75 meters per pixel (m) with substantial cross-track stereo overlap. WAC stereo images from the one-year nominal mission and the first months of the science mission phase are combined to produce a near-global digital terrain model (DTM) with a pixel spacing of 100m, the Global Lunar DTM 100m (GLD100). It covers 79S to 79N latitudes, 98.2% of the entire lunar surface. Mission and Instrument Information: The U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) launched the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) spacecraft to the Moon in June 2009 (Tooley et al., 2010) carrying a variety of instruments that continue to return high-resolution images of the lunar surface from its eccentric polar mapping orbit (Petro et al., 2019). The LRO is a robotic spacecraft designed to acquire data to prepare for and support future human exploration of the Moon. The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) is a system of three cameras mounted on the LRO that capture high resolution black and white images and moderate resolution multi-spectral images of the lunar surface (ASU, 2019). The LROC consists of two narrow-angle cameras (NACs) that provide 0.5 meter-scale panchromatic images over a 5 km swath , a wide-angle camera (WAC) to provide images at a scale of 100 meters/pixel in seven color bands over a 60 km swath, and a Sequence and Compressor System (SCS) supporting data acquisition for both cameras. The LROC data sets are produced by the LROC Team at the Tempe campus of Arizona State University (PDS IMG, 2018). References: Arizona State University (ASU) (2019). About Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. https://www.lroc.sese.asu.edu Petro, N. E., Keller, J. W., Cohen, B. A., & McClanahan, T. P. (2019). Ten years of the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter: Advancing lunar science and context for future lunar exploration. Paper presented at the 50th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, TX. https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2019/pdf/2780.pdf Planetary Data Systems (PDS) Cartography and Imaging Sciences (IMG) (2018). Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/lro_mission.html Robinson, M. S., Brylow, S. M., Humm, D., Lawrence, S. J., Thomas, P. C., Denevi, B. W., Bowman-Cisneros, E., et al. (2010). Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) instrument overview. Space Science Review, 150, 81â124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-010-9634-2 Scholten, F. J., Oberst, J., Matz, K.-D., Roatsch, T., Wählisch, M., Speyerer, E. J., & Robinson, M. S. (2012). GLD100: The near-global lunar 100 m raster DTM from LROC WAC stereo image data. Journal of Geophysical Research, 117(E12). https://doi.org/10.1029/2011JE003926 Tooley, C. R., Houghton, M. B., Saylor Jr., S. S., Peddie, C., Everett, D. F., Baker, C. L., & Safdie, K. N. (2010). Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter mission and spacecraft design. Space Science Review, 150, 23â62. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-009-9624-4
- Purpose
- The stereo-based GLD100 is a valuable topographic representation of the lunar surface and complements the LOLA altimetry data set.
Contact and Distribution
- Format
- Digital Elevation Model, Remote-sensing Data
- Access Constraints
- public domain
- Access Scope
- PDS
- Use Constraints
- Please cite authors
- Series Id
- GLD100
- Edition
- V1.1, August 2013
- Supplemental Information
- http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc/view_rdr/WAC_GLD100, https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2015/pdf/1473.pdf, https://agupubs.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/2013JE004580, http://lroc.sese.asu.edu/about, https://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2011/pdf/2046.pdf
- Native Data Set Environment
- ISIS v3
- Astrogeology Theme
- Image Processing, Photogrammetry, Topography
- Mission Names
- Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter
- Instrument Names
- LROC
- Online Package Link
- https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/moon_lroc_wac_dtm_gld100_118m
- External File Size
- 10 GB
- Online File Link
- https://planetarymaps.usgs.gov/mosaic/Lunar_LRO_WAC_GLD100_DTM_79S79N_100m_v1.1.tif
- Contact Address
- 2255 N. Gemini Drive
- Contact City
- Flagstaff
- Contact State
- AZ
- Contact Postal Code
- 86001
- Contact Email
- astroweb@usgs.gov
- Currentness Reference
- Publication date
- Progress
- In Work
- Update Frequency
- As needed
- Logical Consistency
- The mean relative accuracy is indicated by the mean 3D forward ray intersection accuracy of the final set of points, i.e., 18 m (1 sigma), which corresponds to 0.24 WAC pixel. (Scholten, F., et al., 2012).
- Completeness Report
- The final GLD100 data set extends from 79S to 79N with DTM data covering as much as 99.96% of this latitudinal range. Thus only 0.04% required interpolation (Scholten, F, et al., . 2012)
- Process Description
- For WAC stereo processing the team chose image data from the 604 nm band from images collected in the color mode over a 17 month period [Robinson et al., 2010]. CCD-lines of this band are located near the center of the boresight of the visible optics (1.6 off-nadir). Thus, they provide near-nadir viewing with a minimum influence of residual geometric calibration errors, compared to more off-nadir bands. The respective swath width is about 59.5 km (image width). At the equator, WAC color mode images from subsequent orbits overlap to about 52% and provide a stereo angle of about 33. The stereo angle decreases toward the poles (at 80 latitude it is only 5) from adjacent orbits while the cross-track stereo overlap increases to more than 90% (Scholten, F., et al., 2012). With modifications to account for specific mission and sensor characteristics, a VICAR-base stereo-photogrammetric processing pipeline was developed at German Aerospace Center (DLR, Scholten, F., et al., 2012).
- Source Title
- GLD100: The near-global lunar 100 m raster DTM from LROC WAC stereo image data
- Source Online Linkage
- {http://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/lro/lro-l-lola-2-edr-v1/lrolol_0xxx/data/lola_edr/,http://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/missions/lro/lola.htm,https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/lro_mission.htm,http://wms.lroc.asu.edu/lroc/view_rdr/WAC_GLD100}
- PDS Status
- PDS 3 Archived
- Attribute Accuracy Report
- Best Effort
- Horizontal Positional Accuracy Report
- Accurate to Control Net
- Vertical Positional Accuracy Report
- Accurate to Control Net
Geospatial Information
- Target
- Moon
- System
- Earth
- Minimum Latitude
- -79
- Maximum Latitude
- 79
- Minimum Longitude
- -180
- Maximum Longitude
- 180
- Direct Spatial Reference Method
- Raster
- Object Type
- Grid Cell
- Raster Row Count (lines)
- 47912
- Raster Column Count (samples)
- 109165
- Bit Type (8, 16, 32)
- 16
- Quad Name
- Radius A
- 1737400
- Radius C
- 1737400
- Bands
- 1
- Pixel Resolution (meters/pixel)
- 118.45058759
- Scale (pixels/degree)
- 256
- Map Projection Name
- Equirectangular
- Latitude Type
- Planetocentric
- Longitude Direction
- Positive East
- Longitude Domain
- -180 to 180