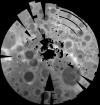
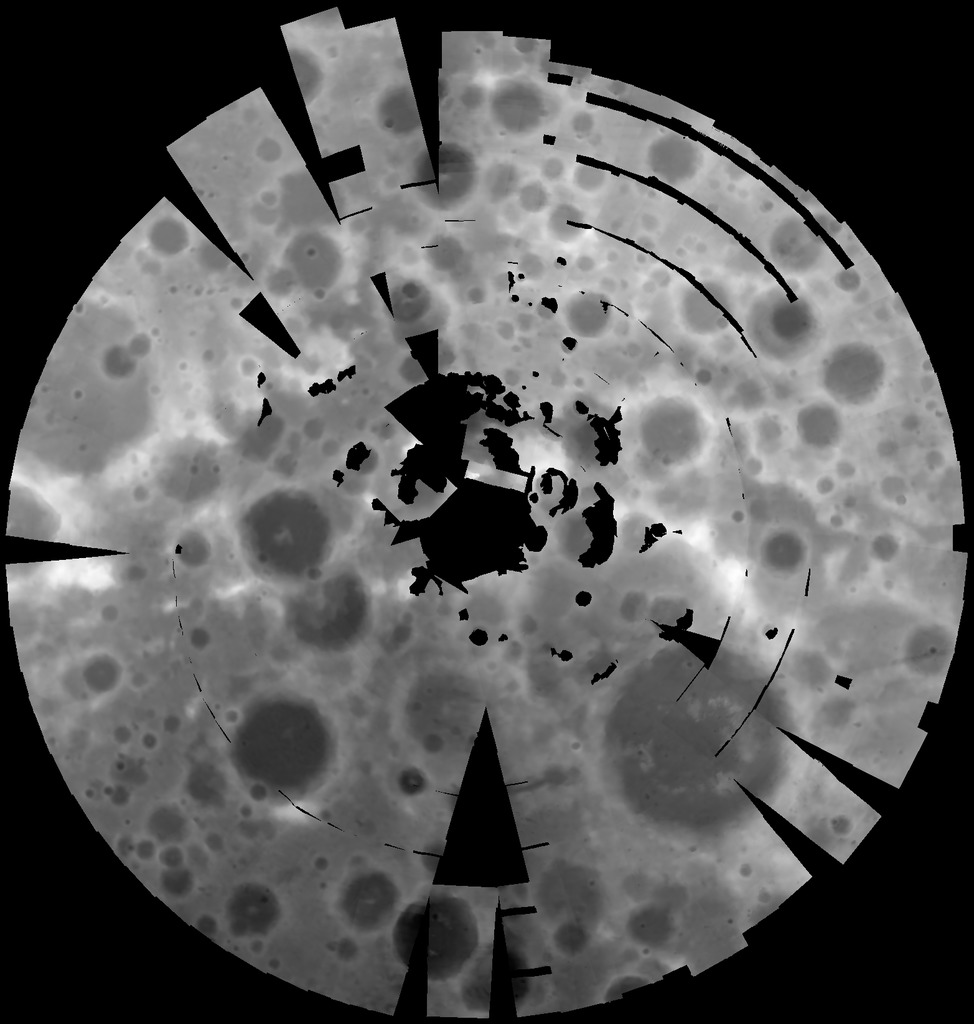
Moon Clementine South Pole DEM 1km
- Primary Authors
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Originators
- Mark Rosiek
- Publisher
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Publication Date
- 2001-09-01
- Abstract
- Product Information: Stereoimagery from the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Clementine mission has been used to produce digital elevation models (DEM) of the Moon, at a scale of approximately one kilometer per pixel (km). These models cover regions poleward of 60 degrees in both hemispheres and reveal topography beyond that covered by the Clementine laser altimeter or Earth-based radar. By combining these polar terrain models with the current Clementine laser altimeter data we have produced a global topographic map of the lunar surface (Cook et al., 2000). Mission and Instrument Information: On January 25, 1994, the Deep Space Program Science Experiment (DSPSE), better known as Clementine, was launched from Vandenburg Air Force Base aboard a Titan IIG rocket, as a joint project between the and was jointly sponsored by the Ballistic Missile Defense Organization (BMDO) of the Dept of Defense and NASA. The objective of the mission was to test sensors and spacecraft components under extended exposure to the space environment and to make scientific observations of the Moon and a near-Earth asteroid (1620 Geographos). After two Earth fly-bys, lunar insertion was achieved on February 19th. Lunar mapping took place over approximately two months in two systematic mapping passes over the Moon. After the spectacular success of the Lunar mapping phase of the mission, Clementine suffered an on-board malfunction on May 7, 1994 that resulted in the activation of its altitude thrusters. This exhausted all the fuel for altitude control and left the spacecraft spinning at 80 revolutions per minute. The result of the malfunction prevented Clementine from performing the planned close fly-by of the near-Earth asteroid Geographos scheduled for August 1994. The main instrumentation on Clementine consisted of four cameras, one with a laser-ranging system. The cameras included an ultraviolet-visual (UVVIS) camera, a long-wavelength infrared (LWIR) camera, the laser-ranger (LIDAR) high-resolution (HIRES) camera, and a near-infrared (NIR) camera. The spacecraft also had two star tracker cameras (A-STAR, B- STAR), used mainly for attitude determination, but they also served as wide-field cameras for various scientific and operational purposes (PDS IMG, 2017). References: Cook, A. C., Watters, T. R., Robinson, M. S., Spudis, P. D., & Bussey, D. B. J. (2000). Lunar polar topography derived from clementine stereoimages. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(E5), 12023-12033. https://doi.org/10.1029/1999JE001083 Nozette, S., Rustan, P., Pleasance, L. P., Kordas, J. F., Lewis, I. T., Park, H. S., Priest, R. E., et al. (1994). The Clementine Mission to the Moon: Scientific Overview. Science, 266(5192), 1835-1839. https://www.doi.org/10.1126/science.266.5192.1835 Planetary Data Systems (PDS) Cartography and Imaging Sciences Node (IMG) (2017). Clementine Mission. https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/clementine_mission.html Rosiek, M. R., Kirk, R., & Howington-Kraus, A. (1999). Lunar topographic maps derived from Clementine imagery. Paper presented at the 30th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, TX. https://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/moon99/pdf/8046.pdf
Contact and Distribution
- Format
- Digital Elevation Model
- Access Constraints
- public domain
- Access Scope
- PDS
- Use Constraints
- None
- Edition
- September 2001
- Supplemental Information
- https://pds.nasa.gov/ds-view/pds/viewProfile.jsp?dsid=CLEM1-L-H-5-DIM-MOSAIC-V1.0, https://pdsimage.wr.usgs.gov/archive/clem1-l-u-5-dim-uvvis-v1.0/cl_4001/document/volinfo.htm, https://isis.astrogeology.usgs.gov
- Native Data Set Environment
- ISIS v3
- Astrogeology Theme
- Topography
- Mission Names
- Clementine
- Instrument Names
- UVVIS
- Online Package Link
- https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/moon_clementine_south_pole_dem_1km
- External File Size
- 10485300
- Online File Link
- http://astropedia.astrogeology.usgs.gov/download/Moon/Clementine/Topography/Lunar_Clementine_SouthPole_DEM_100m_Sep01.cub
- Contact Address
- 2255 N. Gemini Drive
- Contact City
- Flagstaff
- Contact State
- AZ
- Contact Postal Code
- 86001
- Contact Email
- astroweb@usgs.gov
- Currentness Reference
- Publication date
- Progress
- Complete
- Update Frequency
- None planned
- Source Online Linkage
- {https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/volumes/clementine.html,https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/clementine_mission.html}
- Source PDS Archive
- Clementine
- PDS Status
- PDS 4 In Progress
Geospatial Information
- Target
- Moon
- System
- Earth
- Minimum Latitude
- -54.7501564
- Maximum Latitude
- -52.8497543
- Minimum Longitude
- -41.3197823
- Maximum Longitude
- 134.0824585
- Direct Spatial Reference Method
- Raster
- Object Type
- Grid Cell
- Raster Row Count (lines)
- 1646
- Raster Column Count (samples)
- 1565
- Bit Type (8, 16, 32)
- 32
- Quad Name
- LQ-29
- Radius A
- 1737400
- Radius C
- 1737400
- Bands
- 1
- Pixel Resolution (meters/pixel)
- 1000
- Scale (pixels/degree)
- 30.3233504
- Map Projection Name
- Polar Stereographic
- Latitude Type
- Planetocentric
- Longitude Direction
- Positive East
- Longitude Domain
- -180 to 180