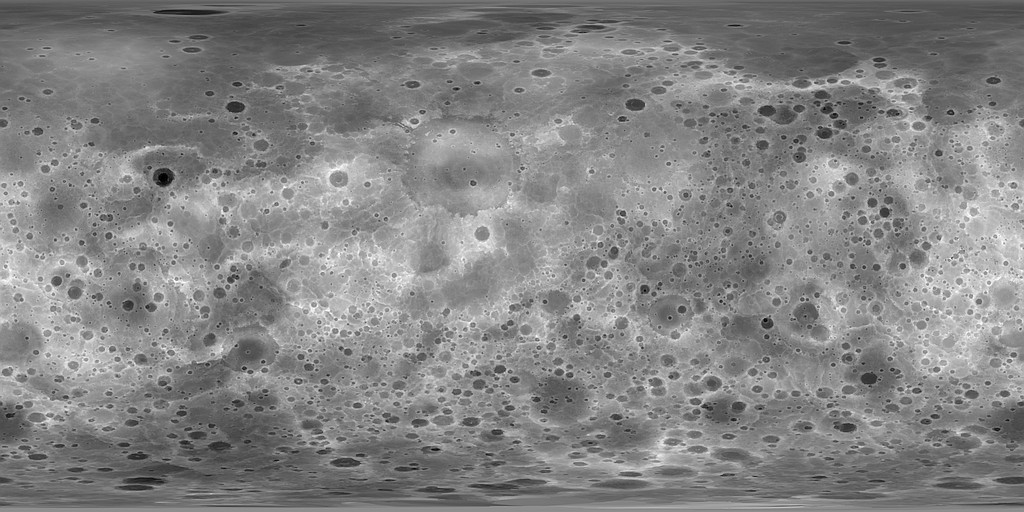
Mercury MESSENGER Global DEM 665m
- Primary Authors
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Originators
- Kris Becker, NASA, Arizona State University, Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, Carnegie Institution for Science
- Publisher
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Publication Date
- 2016-10-21
- Abstract
- Product Information: Using the Integrated Software for Imagers and Spectrometers (ISIS3) and observations from Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS) narrow-angle camera (NAC) and multispectral wide-angle camera (WAC), we derived a global digital elevation model (DEM) of Mercury. We created the global DEM of Mercury from a least-squares bundle adjustment (jigsaw in ISIS3; Becker et al., 2016) of common features, measured as tie point coordinates in overlapping NAC and WAC-G filter images. The resolution of this DEM is 665 meters per pixel (m). The MDIS image inventory contains over 176,000 NAC and WAC-G observations with a very large variety of disparate geometric and illumination characteristics, and we encountered limitations to existing conventional control techniques in ISIS3 that required development of new software and techniques. Our main objectives were to 1) significantly improve image tie point matching accuracy while increasing control point density, and 2) greatly reduce the resources, both human and computer, required to control large image data sets. The new approach utilizes unsupervised image-to-image feature-based matching and control techniques that are well suited for scaling and distribution across compute cluster environments (Becker et al., 2016). This is version 2 of the product derived using a 1-sigma filter applied to the point cloud when processing each output pixel. The original version (1) did not have this filter applied. Mission and Instrument Information: The MErcury Surface, Space Environment, Geochemistry, and Ranging (MESSENGER) spacecraft launched on August 3rd, 2004, it entered orbit around Mercury on March 11, 2011 and ended its mission on April 30th, 2015 when it deliberately plunged into the surface or Mercury. MESSENGER was the first spacecraft to orbit Mercury and had the primary goal of studying the geology, magnetic field, and chemical composition of the planet. The science payload onboard MESSENGER included: Mercury Dual Imaging System (MDIS), Gamma-Ray Spectrometer (GRS), Neutron Spectrometer (NS), X-ray Spectrometer (XRS), Mercury Laser Altimeter (MLA), Mercury Atmospheric and Surface Composition (MACS), Energetic Particle and Plasma Spectrometer (EPPS), and Radio Science experiment (RS). The MDIS instrument suite consists of wide-angle (WAC) and narrow-angle imagers (NAC) situated on a pivot platform that enables the instruments to be pointed in specified directions. References: Becker, K. J., Robinson, M. S., Becker, T. L., Weller, L. A., Edmundson, K. L., Neumann, G. A., Perry, M. E., et al. (2016). First global digital elevation model of Mercury. Paper presented at the 47th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston, TX. https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2016/pdf/2959.pdf Hawkins, S. E., Boldt, J. D., Darlington, E. H., Espiritu, R., Gold, R. E., Gotwols, B., Grey, M. P., et al. (2007). The Mercury Dual Imaging System on the MESSENGER Spacecraft. Space Science Reviews, 131(1â4), 247â338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-007-9266-3 Solomon, S. C., McNutt, R. L., Jr., Gold, R. E., Acuña, M. H., Baker, D. N., Boynton, W. V., Chapman, C. R., et al. (2001). The MESSENGER mission to Mercury: Scientific objectives and implementation. Planetary and Space Science, 49(14-15), 1445-1465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-0633(01)00085-X
- Purpose
- To create a global digital elevation model (DEM) for analysis use and to support image orthorectification.
Contact and Distribution
- Format
- Digital Elevation Model, Raster Data, Topographic Map
- Access Constraints
- None
- Access Scope
- PDS
- Use Constraints
- Please cite authors
- Series Id
- Oct. 2016
- Edition
- V02
- Edition Name
- MSGR_DEM_USG_SC_I_V02
- Supplemental Information
- http://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2016/pdf/2959.pdf, http://messenger.jhuapl.edu/the_mission/mosaics.html, http://messenger.jhuapl.edu/news_room/news-050616.html , http://www.usgs.gov/news/first-global-topographic-map-mercury-released
- Native Data Set Environment
- ISIS v3
- Astrogeology Theme
- Control Network, Image Processing, Remote Sensing, Topography
- Mission Names
- MESSENGER
- Instrument Names
- MDIS, NAC, WAC
- Online Package Link
- https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/mercury_messenger_global_dem_665m
- External File Size
- 506 MB
- Online File Link
- https://planetarymaps.usgs.gov/mosaic/Mercury_Messenger_USGS_DEM_Global_665m_v2.tif
- Contact Address
- 2255 N. Gemini Drive
- Contact City
- Flagstaff
- Contact State
- AZ
- Contact Postal Code
- 86001
- Contact Email
- astroweb@usgs.gov
Data Status and Quality
- Time Period of Content (start)
- 2011-03-29
- Time Period of Content (stop)
- 2015-04-30
- Currentness Reference
- Ground condition
- Progress
- Complete
- Update Frequency
- As needed
- Logical Consistency
- The initial step in creation of a control network is the identification of overlapping areas between images from ephemeris data (e.g., spacecraft position and pointing attitude from mission Navigation and Ancillary Information Facility SPICE data). SPICE data can contain uncertainties that limit accurate identification of overlap between images and precise measurement of image tie points. Control point networks contain tie points that are sample/line coordinates with geometric locations (derived from SPICE) that are automatically measured across the overlapping image areas. Tie point locations are typically randomly placed on images, often in areas of low contrast and shadows.
- Completeness Report
- Global coverage
- Process Description
- This is version 2 of the product derived using a 1-sigma filter applied to the point cloud when processing each output pixel. The original version (1) did not have this filter applied. From 176, 352 images, we selected a subset limited by pixel scale (75 to 800 m/pixel; NAC (64, 086) and WAC-G (37, 091) images), and successfully controlled 100, 432 images (63, 536 NAC, 36, 896 WAC-G) to sub-pixel accuracy (0.86 average pixel residual from the bundle adjustment). We used the efficient FASTX feature detector that is well suited for identification of landforms. A SIFT descriptor extractor and BruteForce matcher was used to create the control measures from overlapping image pairs. The final global control network contained 12, 596, 336 control points and 94, 745, 475 tie point measurements. This is the largest control network ever processed in ISIS3. A preliminary comparison of the global control point cloud with the Mercury Laser Altimeter/Radio Science DEM appears elsewhere. We interpolated a global DEM at 64 pixels/degree (665 m/pixel) directly from the control network point cloud (an irregularly spaced dataset) stored in a kd-tree structure by selecting the nearest 11 points closest to the center output DEM pixel geometric coordinate. From those 11 points, a 1.0-standard-deviation filter centered about the median radius was applied to eliminate outliers. The median radius from the remaining points was selected as the output DEM radius value. A series of averaging filters smoothed the final DEM relative to a datum radius of 2439.4 km.
- Source Title
- MESSENGER Online Data Volumes
- Source Online Linkage
- {https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/volumes/mess.html,https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/messenger_mission.html}
- Source PDS Archive
- MESSENGER
- PDS Status
- PDS 3 Archived
- Attribute Accuracy Report
- Best Effort
Geospatial Information
- Target
- Mercury
- Minimum Latitude
- -90
- Maximum Latitude
- 90
- Minimum Longitude
- 0
- Maximum Longitude
- 360
- Direct Spatial Reference Method
- Raster
- Object Type
- Grid Cell
- Raster Row Count (lines)
- 11520
- Raster Column Count (samples)
- 23040
- Bit Type (8, 16, 32)
- 16
- Quad Name
- Radius A
- 2439400
- Radius C
- 2439400
- Bands
- 1
- Pixel Resolution (meters/pixel)
- 665.24315270546
- Scale (pixels/degree)
- 64
- Vertical Coordinate System Units
- Meters
- Map Projection Name
- Equirectangular
- Latitude Type
- Planetocentric
- Longitude Direction
- Positive East
- Longitude Domain
- 0 to 360