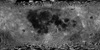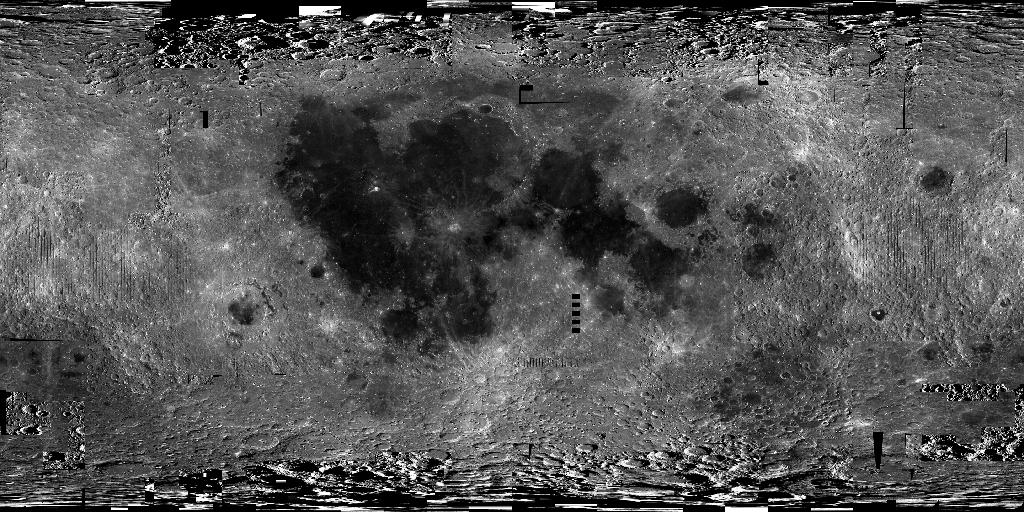
This near-global lunar mosaic (474 m/pixel, 64 pixel/degree) was generated using data from the SELenological and Engineering Explorer (SELENE) “Kaguya” Terrain Camera (TC) instrument. TC source data originated as map-projected tiles at ~10 meters per pixel (m) spatial resolution. The five mosaics were produced at 64 pixels/degree (474 meter/pixel spatial resolution) and include two versions each of both low-sun Morning (early or right-to-left low-angle solar illumination) and Evening (late or left-to-right solar illumination) illuminations, along with a merged best-of “Ortho” version, a Kaguya team term indicating simulated vertical illumination.
Science Impact and Relevance
With Kaguya DTM coregistration, the source tiles match very well with the positions of the Apollo Lunar Retroreflector array (-17 to 5 m longitude, -20 to 48 m latitude, 3 to 5 m elevation; [6]). Quality of registration, high spatial resolution, and image clarity are impressive and these data provide excellent complements to color data such as those from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Wide Angle Camera (LROC WAC) and the Clementine Ultraviolet/Visible (UVVIS) mosaic products for geologic studies, mapping, and morphologic and structural analyses of the lunar surface.
One of the primary goals for the Kaguya mission was to augment the high-resolution image data available for the lunar surface, particularly the far side. At 10 m/pixel globally, the TC data effectively bridge the resolution gap between the LROC WAC (100 m/pixel) and the LROC NAC (~1 m/pixel) data and thus they provide invaluable contextual information. The data have enabled discoveries of relatively small lunar features such as lava-tube skylights [8], small impact craters used to determine relative age [9], lack of exposed ice at Shackleton crater (lunar south pole, [1]) and mare eruption ages [10]. Availability of the global TC data will greatly facilitate a wide variety of lunar studies, including relative and absolute chronology (e.g., crater counting), geologic mapping, structural analyses, site characterization, etc. to better understand the Moon’s geologic record. The low-sun and dual-illumination TC data provide unmatched morphologic information that support geologic and feature mapping at local to regional scales (~1:50,000 to ~1:250,000). The availability of coverage at multiple illuminations will help to ensure that any given site can be studied.
References
[1] Haruyama, J. et al. and the LISM Working Group (2008) Earth Planets Space, 60, 243-255. [2] Kato, M., Y. Takizawa, and S. Sasaki (2007) LPS XXXVIII, Abstract #1402. [3] Ohtake, M., et al. (2008) Earth Planets Space, 60, 257-264. [4] Matsunaga, T., et al. (2008) Geophys. Res. Letters. 35, L23201, doi:10.1029/2008GL035868. [5] Kato, M., Y. Takizawa, and S. Sasaki, Selene Project Team (2006) LPS XXXVII, Abstract #1233. [6] Haruyama, J., S. Hara, et al. (2012) LPS XLIII, Abstract #1200. [7] Kestay, L., et al., this volume. [8] Haruyama, J., et al. (2009) Geophys. Res. Letters, 36, L21206, doi:10.1029/2009GL040635 [9] Morota, T., et al. (2009) Meteoritics and Planetary Science 44, 1115-1120. [10] Cho, Y., et al. (2012) Geophys. Res. Letters, doi:10.1029/2012GL051838.