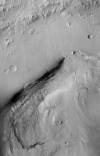
Mars MSL Gale Merged Orthophoto Mosaic 25cm
- Primary Authors
- Fred J. Calef III and Timothy Parker
- Originators
- JPL-Caltech, NASA, USGS Astrogeology Science Center, University of Arizona
- Publisher
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Publication Date
- 2016-10-20
- Abstract
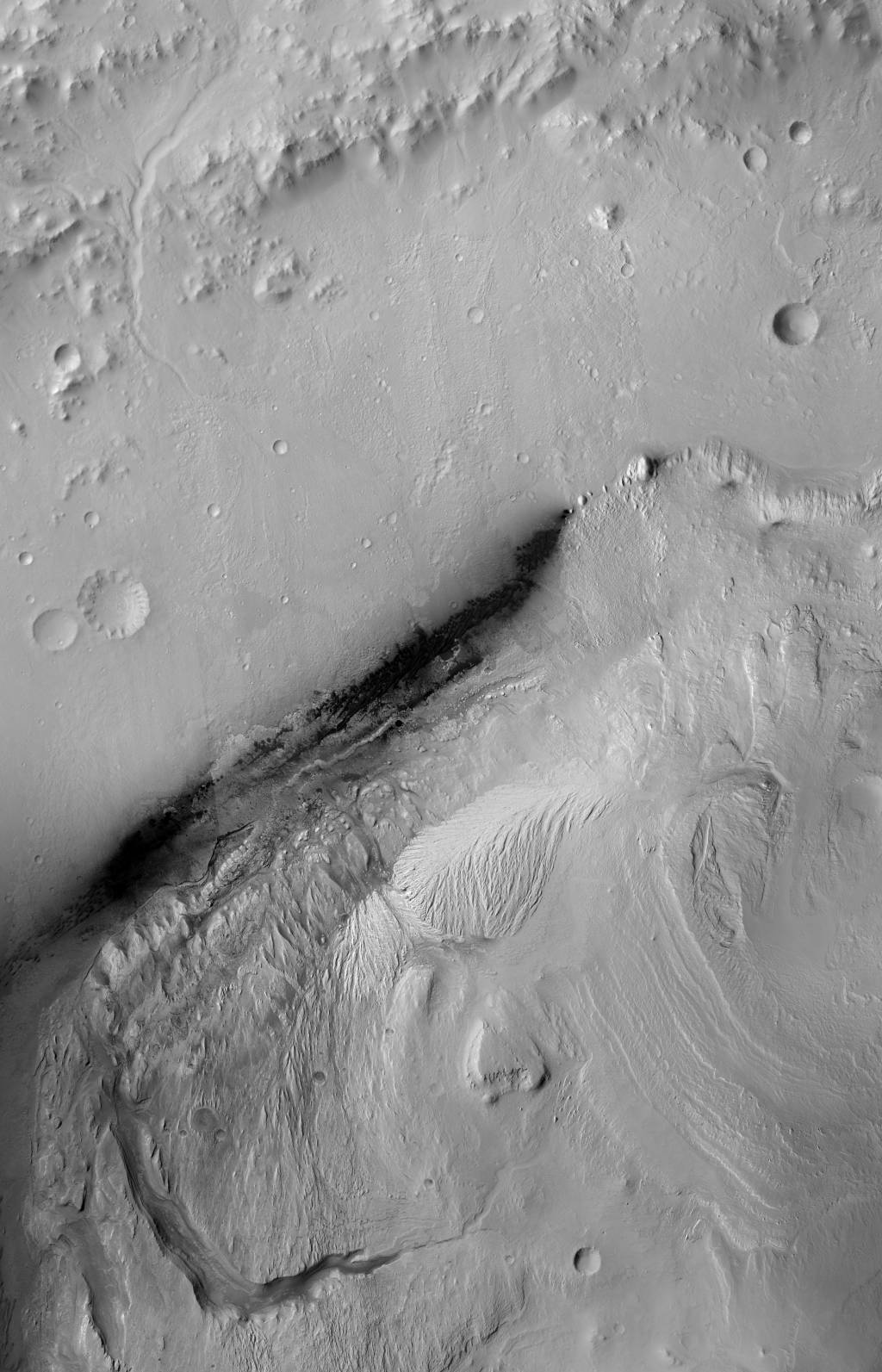
- Grayscale Product Information: This basemap was initially created as an assessment tool for the entry, descent, and landing (EDL) analysis conducted by the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) engineering team to assess Gale crater as a safe landing site for the rover. The image is built up from High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) orthophotos, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) Context Camera (CTX) map-projected images, and High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) orthophotos all tied to a Mars Orbiter Laster Altimeter (MOLA) base via the HRSC. Georeferencing was manually done from CTX to HRSC, then HiRISE to CTX or overlapping pre-georefererenced HiRISE. Pixel resolution is 25 centimeters per pixel (cm). Download is the link above or: https://asc-pds-services.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mosaic/MSL_Gale_Orthophoto_Mosaic_25cm_v3.tif (23 GB, lossless) Orthophotos using the following HiRISE stereo pairs were used in the creation of this basemap (USGS processing designations/names in quotes): ESP_024234_1755, ESP_024300_1755 'West Gap'; PSP_009650_1755, PSP_009716_1755, 'West'; PSP_010573_1755, PSP_010639_1755, 'Center'; PSP_009505_1755, PSP_009571_1755, 'G2' (Landed in this stereo pair.); ESP_011417_1755, ESP_011562_1755, 'East'; ESP_018854_1755, ESP_018920_1755, 'West of Center'; ESP_023957_1755, ESP_024023_1755, 'Center Gap'; ESP_024102_1755, ESP_025368_1755, 'East Gap'; PSP_009149_1755, PSP_009294_1755, 'Traverse'; ESP_012551_1755, ESP_012841_1755, 'T2'; PSP_001488_1755, PSP_001752_1755, 'T1'; ESP_019698_1755, ESP_019988_1755, 'T3' NEW (July 2025) Color Mosaic now available The HiRISE 78 quad color basemap is composed of several HiRISE RGB color strips georectified using thousands of manually placed tie-points, blended and then fused using Adobe Photoshop to the MSL mission HiRISE RED orthophoto mosaic (this page) to provide corrected cartographic placement on Mars and for rover operations. This mosaic was slightly sharpened in GIMP (unsharp mask, v 2.10.20) to enhance feature quality at the finest scales. Note: This version was converted to a Jpeg compressed COG for streaming (Quality = 85, near lossless). Authorship order for this color version is Timothy Parker and Fred J. Calef III. Color mosaic download: https://asc-pds-services.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mosaic/Mars/MSL/MSL_Gale_HiRISE-LRGB_78quads_sharp_cog.tif (~1 GB) Mission and Instrument Information: Mars Global Surveyor was the first successful U.S. mission launched to Mars since the Viking mission in 1976 (Albee et al., 2001). After a 20-year absence at the planet, MGS launched on November 7, 1996 and ushered in a new era of Mars exploration with its five science investigations. The Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) created the most accurate global topographic map of any planet in the solar system, giving scientists elevation maps precise to within about 30 centimeters (1 foot) in the vertical dimension. Data from the laser altimeter identified pathways for the flow of past water and the locations, sizes, and volumes of watersheds (NASA JPL, 2010). Mars Express is a mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) it launched in June 2003 onboard a Soyuz-Fregat launcher from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan. The High-Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC) is imaging the entire planet in full color, 3D and with a resolution of about 10 meters. Selected areas will be imaged at 2-meter resolution. One of the camera's greatest strengths will be the unprecedented pointing accuracy achieved by combining images at the two different resolutions. Another will be the 3D imaging which will reveal the topography of Mars in full color (ESA, 2010). Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter launched August 12, 2005 and arrived at Mars on March 10, 2006. The mission has shown unprecedented detail in orbital images of Mars. The Context Camera (CTX) is currently orbiting Mars and acquiring grayscale (black & white) images at 6 meters per pixel scale over a swath 30 kilometers wide. The Hi Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE camera) is a pushbroom imaging system featuring a 0.5 m aperture telescope with a 12 m focal effective length and 14 CCD detectors capable of generating images of up to 20,000 cross-scan observation pixels and 65,000 unbinned scan lines. The HiRISE instrument capabilities include the acquisition of observations of the Mars surface from orbit with a ground sampling dimension between 25 and 32 cm (PDS IMG, 2018). The Mars Science Laboratory mission's Curiosity rover, the most technologically advanced rover ever built, landed in Mars' Gale Crater in August, 2012 using a series of complicated landing maneuvers never before attempted. The specialized landing sequence, which employed a giant parachute, a jet-controlled descent vehicle and a bungee-like apparatus called a "sky crane," was devised because tested landing techniques used during previous rover missions could not safely accommodate the much larger and heavier rover (PDS IMG, 2018b; NASA, 2019). Reference: Albee, A. L., Arvidson, R. E., Palluconi, F., & Thorpe, T. (2001). Overview of the Mars Global Surveyor mission. Journal of Geophysical Research, 106(E10), 23291-23316. https://doi.org/10.1029/2000JE001306 European Space Agency (ESA) (2010). Mars Express. Mars Express Orbiter Instruments. https://www.esa.int/Science_Exploration/Space_Science/Mars_Express/Mars_Express_instruments Kirk, R. L., Howington-Kraus, E., Rosiek, M. R., Anderson, J. A., Archinal, B. A., Becker, K. J., HiRISE Team, et al. (2008). Ultrahigh resolution topographic mapping of Mars with MRO HiRISE stereo images: Meter-scale slopes of candidate Phoenix landing sites. Journal of Geophysical Research, 113(E3). https://doi.org/10.1029/2007JE003000 National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) (2019). Mars Curiosity Rover. Timeline: Entry, Descent, and Landing. https://mars.nasa.gov/msl/timeline/edl/ National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) (2010). Mars Global Surveyor. https://mars.nasa.gov/mgs/overview/ Planetary Data Systems (PDS) Cartography and Imaging Sciences (IMG) (2018a). Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO). https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/mro_mission.html Planetary Data Systems (PDS) Cartography and Imaging Sciences (IMG) (2018b). Mars Science Laboratory (MSL). https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/msl_mission.html Recommended Citation: Calef III, F. J., & Parker, T. (2016). MSL Gale Merged Orthophoto Mosaic. PDS Annex, U.S. Geological Survey. https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/mars_msl_gale_merged_orthophoto_mosaic_25cm
- Purpose
- This image serves as the basemap for science and engineering operations conducted by the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL), aka Curiosity rover, on Mars.
Contact and Distribution
- Format
- Color
- Access Constraints
- Please credit authors
- Access Scope
- PDS
- Use Constraints
- None
- Series Id
- Orthophoto Mosaic
- Edition
- version 3
- Edition Name
- MSL_Gale_Orthophoto_Mosaic_25cm
- Supplemental Information
- http://mars.nasa.gov/msl/, http://hrscview.fu-berlin.de/, http://mars.nasa.gov/mro/mission/instruments/ctx/, http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/, http://sci.esa.int/mars-express/42328-hrsc-high-level-data-products-available/, https://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Science/Mars_Express/The_mission, http://hirise.lpl.arizona.edu/
- Native Data Set Environment
- ESRI Arcinfo
- Astrogeology Theme
- Exploration, Image Processing, Landing sites
- Mission Names
- Mars Express, Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
- Instrument Names
- CTX, HRSC, HiRISE
- Digital Product?
- yes
- Online Package Link
- https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/mars_msl_gale_merged_orthophoto_mosaic_25cm
- Checksum
- e1b8670b605eb593dc1d0551f6c45b64
- External File Size
- 23 GB
- Online File Link
- https://asc-pds-services.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mosaic/MSL_Gale_Orthophoto_Mosaic_25cm_v3.tif
- Contact Address
- 2255 N. Gemini Drive
- Contact City
- Flagstaff
- Contact State
- AZ
- Contact Postal Code
- 86001
- Contact Email
- astroweb@usgs.gov
- Logical Consistency
- HRSC is controlled to MOLA and thus only as accurate as MOLA (~100m horizontal and ~1 m vertical accuracy).
- Completeness Report
- Where HiRISE coverage is lacking either CTX and then HRSC coverage was used.
- Process Description
- Georeferencing was manually done from CTX to HRSC (already registered to MOLA), then HiRISE to CTX.
Lineage
- Process Date
- 2011-01-01
- Source Title
- MRO HiRISE and CTX and Mars Express HRSC Archives
- Source Online Linkage
- {https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/volumes/mro.html,http://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/missions/mgs/mola.html,http://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/missions/mars_express/hrsc.htm,http://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/missions/mars_express/,https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/mro_mission.html,http://pds-geosciences.wustl.edu/missions/mgs/index.htm}
- Source PDS Archive
- Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
- PDS Status
- PDS 3 Compatible
- Horizontal Positional Accuracy Report
- Accurate to Control Net
- Vertical Positional Accuracy Report
- Accurate to Control Net
Geospatial Information
- Target
- Mars
- System
- Mars
- Feature Name
- Gale
- Minimum Latitude
- -5.249525
- Maximum Latitude
- -4.068583
- Minimum Longitude
- 137.094719
- Maximum Longitude
- 137.853896
- Direct Spatial Reference Method
- Raster
- Object Type
- Grid Cell
- Raster Row Count (lines)
- 280000
- Raster Column Count (samples)
- 180000
- Bit Type (8, 16, 32)
- 8
- Quad Name
- MC-23
- Radius A
- 3396190
- Radius C
- 3396190
- Control Net
- MOLA
- Bands
- 1
- Pixel Resolution (meters/pixel)
- 0.25
- Vertical Coordinate System Units
- Meters
- Map Projection Name
- Equirectangular
- Latitude Type
- Planetocentric
- Longitude Direction
- Positive East
- Longitude Domain
- -180 to 180