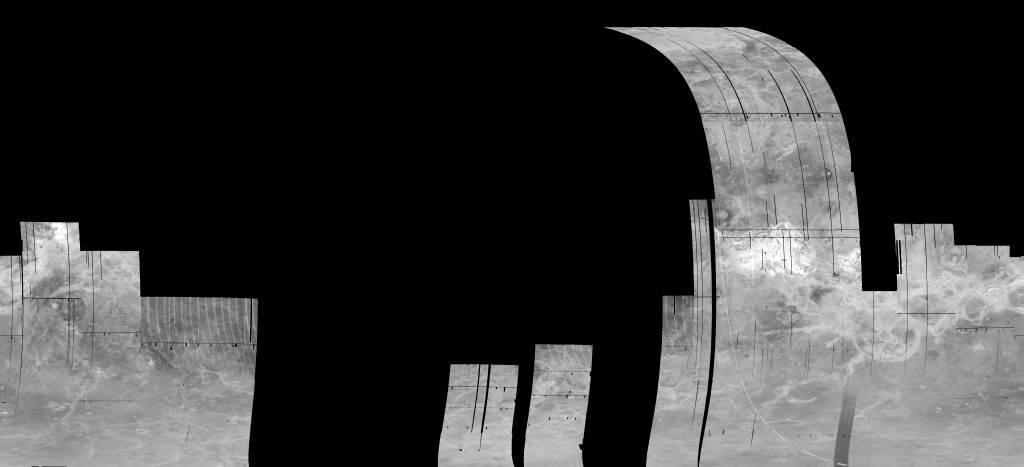
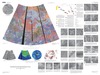
Venus Magellan SAR FMAP Right Look Global Mosaic 75m
- Primary Authors
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Originators
- National Space Science Data Center
- Publisher
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Publication Date
- 2015-08-01
- Abstract
- Product Information: This mosaic was created from the Magellan Full resolution Basic Image Data Records (F-BIDRs), the highest resolution radar images of the Venus surface (~75 meters per pixel [m]). Even though called global, this mosaic only covers 17% of the planet. For a smaller download, this base is available for processing (clipping and format conversion) using the Map-A-Planet 2 "processing" button on the right. Pixel values (DNs) are 8 bit based on this scaling factor and offset. SCALING_FACTOR = 0.2 OFFSET = -20.2 NOTE = "DN = 5 * (MIN(MAX(RV ,-20),30) + 20) + 1, where RV = specific radar cross-section divided by the Muhleman Law value: SIGMA0(THETA) = 0.0118 COS(THETA) / ((SIN(THETA) + 0.111 COS(THETA))**3) where THETA is the scattering angle." Mission and Instrument Information: The Magellan Mission to Venus launched on May 4, 1989 on board the Space Shuttle Atlantis. The spacecraft arrived at Venus on August 10th, 1990 and was inserted into a near-polar elliptical orbit. The primary mission requirements were to map at least 70% of the surface at a resolution better than 300 meters/pixel and to determine the global relief at such a resolution as to facilitate detailed analysis of tectonic, volcanic, eolian, and impact features. Magellan successfully completed four mapping cycles at Venus. The first mapping cycle lasted from mid-September 1990 to mid-May 1991 focused on fulfilling the primary mission requirements. The second mapping cycle was from mid-May 1991 to mid-January 1992 and was dedicated to filing in gaps in the cycle 1 coverage and obtaining coverage of the south polar region; this cycle resulted in 54% of surfaced coverage and increased the cumulative coverage of the mission to 96%. Cycle 3 was from mid-January to mid-September 1992 and focused on acquiring stereo image coverage; this cycle resulted in about 21% surface coverage and increased total surface coverage to 98%. Cycle 4 was dedicated to gravity observations and as such did not add to the cumulative coverage of imagery taken by the spacecraft (Ford, et al, 1993). Because Venus is shrouded by a dense, opaque atmosphere, conventional optical cameras cannot be used to image its surface. Instead, Magellan's imaging radar uses bursts of microwave energy somewhat like a camera flash to illuminate the planet's surface. The radar pulses are not sent directly downward but rather at a slight angle to the side of the spacecraft--the radar is thus called "side-looking radar." In addition, special processing techniques are used on the radar data to result in higher resolution as if the radar had a larger antenna, or "aperture"; the technique is thus often called "synthetic aperture radar" (SAR). The Magellan SAR is a side-looking radar system. Radar pulses are not sent directly downward but rather at a slight angle to the side of the spacecraft. In the case of Right-Look Magellan SAR data, the radar system was sending signals to the right of the spacecraft. The SAR operated in this right-looking mode during cycle 2 of the mission. References: Ford, J. P., Plaut, J. J., Weitz, C. M., Farr, T. G., Senske, D. A., Stofan, E. R., Michaels, G., & Parker, T. J. (1993). Guide to Magellan Image Interpretation. JPL Publication 93-24 pp. 1-18. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19940013181.pdf Ford, J. P., Blom, R. G., Crisp, J. A., Elachi, C., Farr, T. G., Saunders, R. S., Theilig, E. E., et al. (1989). Spaceborne Radar Observations, A guide for Magellan radar-image analysis. JPL Publication 89-41. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19900013510.pdf
- Purpose
- To create a mosaic of the SAR images tile generated during cycle 2 of the Magellan mission.
Contact and Distribution
- Format
- Global Mosaic, Raster Data, Remote-sensing Data
- Access Constraints
- public domain
- Access Scope
- PDS
- Use Constraints
- None
- Supplemental Information
- https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/software/MGN_SAR_UserGuide.pdf
- Native Data Set Environment
- ISIS v3
- Astrogeology Theme
- Geomorphology, Remote Sensing, Volcanism
- Mission Names
- Magellan
- Instrument Names
- SAR
- Online Package Link
- https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/venus_magellan_sar_fmap_right_look_global_mosaic_75m
- External File Size
- 110 GB
- Online File Link
- https://asc-pds-services.s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/mosaic/Venus_Magellan_RightLook_mosaic_global_75m.tif
- Access Instructions
- Due to the file size, this mosaic may be difficult to download using a browser. Wget or other download tool should work better. This can also be cropped and map projected using MAP2 (the process button on the right).
- Contact Address
- 2255 N. Gemini Drive
- Contact City
- Flagstaff
- Contact State
- AZ
- Contact Postal Code
- 86001
- Contact Email
- [email protected]
Data Status and Quality
- Time Period of Content (start)
- 1990-09-15
- Time Period of Content (stop)
- 1992-09-14
- Currentness Reference
- Ground condition
- Progress
- Complete
- Update Frequency
- None planned
- Logical Consistency
- right-looking (Magellan cycle 2).
- Completeness Report
- This map contains about 55% of the planet
- Process Description
- Software to reproject, mosaic, and do cosmetic seam removal to put the image data in FMAP format was developed by Kay Edwards and Tracie Sucharski (USGS). Cartographic processing was done by Robert Sucharski (USGS).
- Source Title
- Magellan Venus FMAPs (PDS), PSPG-00177
- Source Online Linkage
- {https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/volumes/magellan.html#mgnSAR,https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/volumes/magellan.html#mgnFMAP,http://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/magellan_mission.html}
- PDS Status
- PDS 3 Archived
- Attribute Accuracy Report
- Accurate to Control Net
Geospatial Information
- Target
- Venus
- Minimum Latitude
- -80
- Maximum Latitude
- 84
- Minimum Longitude
- -180
- Maximum Longitude
- 180
- Direct Spatial Reference Method
- Raster
- Object Type
- Grid Cell
- Raster Row Count (lines)
- 230948
- Raster Column Count (samples)
- 506928
- Bit Type (8, 16, 32)
- 8
- Quad Name
- Radius A
- 6051000
- Radius C
- 6051000
- Bands
- 1
- Pixel Resolution (meters/pixel)
- 75
- Scale (pixels/degree)
- 1408.1316
- Map Projection Name
- Equirectangular
- Latitude Type
- Planetocentric
- Longitude Direction
- Positive East
- Longitude Domain
- -180 to 180