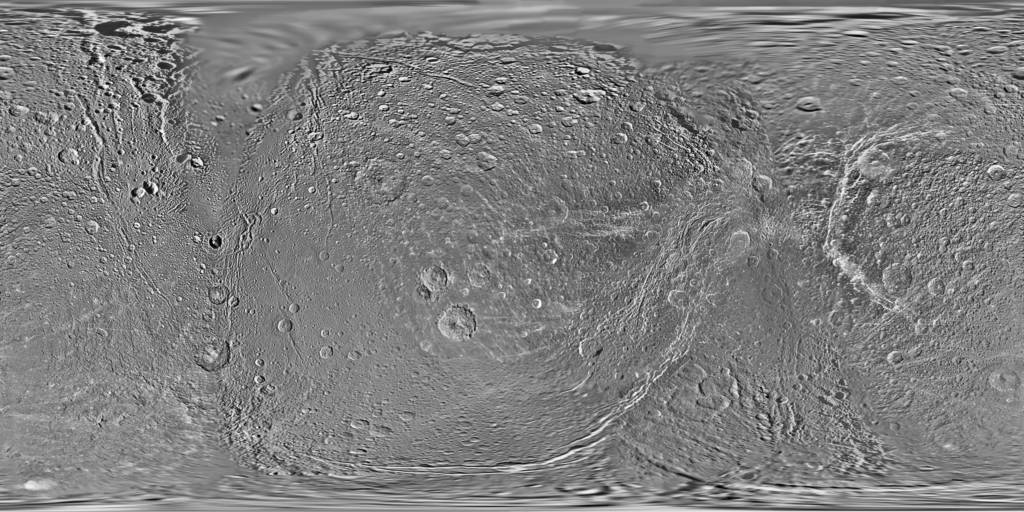
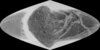
Dione Cassini - Voyager Global Mosaic 154m
- Originators
- NASA, JPL, Space Science Institute
- Publisher
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Abstract
- Product Information: This global map of Saturn's moon Dione was created using images taken during flybys by NASA's Cassini spacecraft. Images from NASA's Voyager mission fill the gaps in Cassini's coverage. An extensive system of bright ice cliffs created by tectonic fractures adorns the moon's trailing hemisphere, which is centered on 270 degrees west (Schneck, 2016). The map is a Simple Cylindrical (equidistant) projection and has a scale of 153 meters per pixel (500 feet) at the equator (Roatsch et al., 2016). The resolution of the map is 64 pixels per degree; 154 meters per pixel (m) . The mean radius of Dione used for projection of this map is 563 kilometers (350 miles). Like the 2008 version of the map (PIA08413), this updated map has been shifted west by 0.6 degrees of longitude, compared to the 2006 version of the map (PIA08341), in order to conform to the International Astronomical Union longitude system convention for Dione. Mission and Instrument Information: The Voyager I space craft launched September 5, 1977 and passed through the Saturnian system on November 12, 1981. Voyager 2 launched August 20, 1977 and made a similar encounter with the Saturnian system, returning more images of the satellites. The space craft carried both wide- and narrow- angle cameras, which were able to capture and return moderate- to high- resolution images of the satellites Rhea, Dione, Enceladus, Mimas, Tethys, and Iapetus. The rapid speed of the space craft as it approached the satellites resulted in significant mis-matches of image resolution and image blur (Greely & Batson, 2007; Batson, 1984). The Cassini-Huygens mission was a joint endeavor between the Italian Space Agency, the European Space Agency (ESA) and National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The Cassini-Huygens mission launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Base in Florida on October 15, 1997 and ended on September 15, 2017 when Cassini began its Final Entry into Saturnâs Atmosphere. The primary mission ran from July 2004 â June 2008, the first mission extension (Equinox) was from July 2008- October 2010 and was followed by a final extended mission (Solstice) from October 2010 â September 2017. The imaging team consists of scientists from the US, England, France, and Germany. The imaging operations center and team lead (Dr. C. Porco) are based at the Space Science Institute in Boulder, Colorado, USA. The Cassini Imaging Science Subsystem (ISS) consists of two framing cameras. The narrow angle camera is a reflecting telescope with a focal length of 2000 mm and a field of view of 0.35 degrees. The wide-angle camera is a refractor with a focal length of 200 mm and a field of view of 3.5 degrees. The stated objective of the ISS is to obtain global coverage for all medium-sized icy satellites with a resolution better than 1 km/pixel and high-resolution images of selected areas (Porco, 2004). This goal was achieved with image sequences obtained during close flybys supplemented by images from greater distances to complete the coverage (Roatsch, 2016). References: Batson, R. (1984). Voyager 1 and 2 Atlas of Six Saturnian Satellites (NASA-SP-474). Washington, DC: National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19840027171.pdf Greely, R., & Batson, R. (2007). Planetary Mapping. (ISBN 0-521-30774-0). New York, NY: Cambridge University Press. Roatsch, T., Kersten, E., Matz, K.-D., Scholten, F., & Porco, C. C. (2016). Cartography of the medium-sized saturnian satellites based on Cassini-ISS images. Paper presented at the Enceladus and the Icy Moons of Saturn Conference, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Boulder, CO. https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/enceladus2016/pdf/3032.pdf Schnek, P. (2016). Global color and cartographic mapping of Saturnâs midsize icy moons. Paper presented at the Enceladus and the Icy Moons of Saturn Conference, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Boulder, CO. https://www.hou.usra.edu/meetings/enceladus2016/pdf/3053.pdf
- Purpose
- To create a mosaic of Dione for planetary studies.
Contact and Distribution
- Format
- Global Mosaic, Raster Data, Remote-sensing Data
- Access Constraints
- Public domain
- Access Scope
- PDS
- Use Constraints
- Please cite authors
- Edition
- 2010
- Supplemental Information
- http://www.ciclops.org/view/6264/Map_of_Dione_-_February_2010?js=1, https://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/cassini/overview/, http://ciclops.org
- Native Data Set Environment
- ISIS v3
- Astrogeology Theme
- Geomorphology, Remote Sensing, Satellites
- Mission Names
- Cassini-Huygens, Voyager
- Instrument Names
- SSI
- Online Package Link
- https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/dione_cassini_voyager_global_mosaic_154m
- External File Size
- 254 MB
- Online File Link
- https://planetarymaps.usgs.gov/mosaic/Dione_Cassini_Voyager_mosaic_global_154m.tif
- Contact Address
- 2255 N. Gemini Drive
- Contact City
- Flagstaff
- Contact State
- AZ
- Contact Postal Code
- 86001
- Contact Email
- astroweb@usgs.gov
- Progress
- Complete
- Update Frequency
- As needed
- Logical Consistency
- Like the 2008 version of the map (PIA08413), this updated map has been shifted west by 0.6 degrees of longitude, compared to the 2006 version of the map (PIA08341), in order to conform to the International Astronomical Union longitude system convention for Dione.
- Completeness Report
- Images from NASA's Voyager mission fill the gaps in Cassini's coverage.
- Source Online Linkage
- {https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/volumes/iss.html,https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/volumes/voyager.html#vgrISSEDR-J,https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/cassini_mission.html,https://pds-imaging.jpl.nasa.gov/portal/voyager_mission.html}
- Source PDS Archive
- Cassini
- PDS Status
- PDS 3 Like
- Attribute Accuracy Report
- Best Effort
Geospatial Information
- Target
- Dione
- System
- Saturn
- Minimum Latitude
- -90
- Maximum Latitude
- 90
- Minimum Longitude
- -180
- Maximum Longitude
- 180
- Direct Spatial Reference Method
- Raster
- Object Type
- Grid Cell
- Raster Row Count (lines)
- 11520
- Raster Column Count (samples)
- 23040
- Bit Type (8, 16, 32)
- 8
- Quad Name
- Radius A
- 563000
- Radius C
- 563000
- Bands
- 1
- Pixel Resolution (meters/pixel)
- 153.53443263638
- Scale (pixels/degree)
- 64
- Map Projection Name
- Simple Cylindrical
- Latitude Type
- Planetocentric
- Longitude Direction
- Positive West
- Longitude Domain
- -180 to 180