Clementine Lunar Control Network
- Originators
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Publisher
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Abstract
-
The Clementine Lunar Control Network (CLCN) includes 543,245 measurements of 271,634 points on 43,871 Clementine 750-nm images-the largest planetary control network ever computed. It was completed at RAND by Merton Davies and Tim Colvin in 1997, in cooperation with the U. S. Geological Survey (Flagstaff). The purpose of this network was to determine the geometry for the Clementine 750-nm Base map Mosaic (CBM) [set of 15 CDs, USGS, 1997]. The geometry of that mosaic was used to produce the Clementine UVVIS digital image model [set of 78 CDs, USGS, 1999; Eliason et al., 1999] and the Near-Infrared (NIR) Global Multispectral Map of the Moon from Clementine [set of 78 CD's, USGS, in publication; Eliason et al., 2003]. Obviously many researchers use these products. Through such use, these products and the underlying CLCN in effect define the generally accepted current coordinate system for reporting and describing the location of lunar coordinates. However, no specific publication describes the CLCN itself.
The files from this network were transferred to the U. S. Geological Survey in 2000, as part of the transfer of geodesy work from RAND to USGS in 2000-2001 [Archinal et al., 2000, 2001, 2002a, 2002b, 2003]. They have also been made available upon request from either RAND or USGS. The Clementine spacecraft position and solved-for camera pointing angles (i.e. SPICE data) of the CLCN are also available as part of the USGS ISIS package.
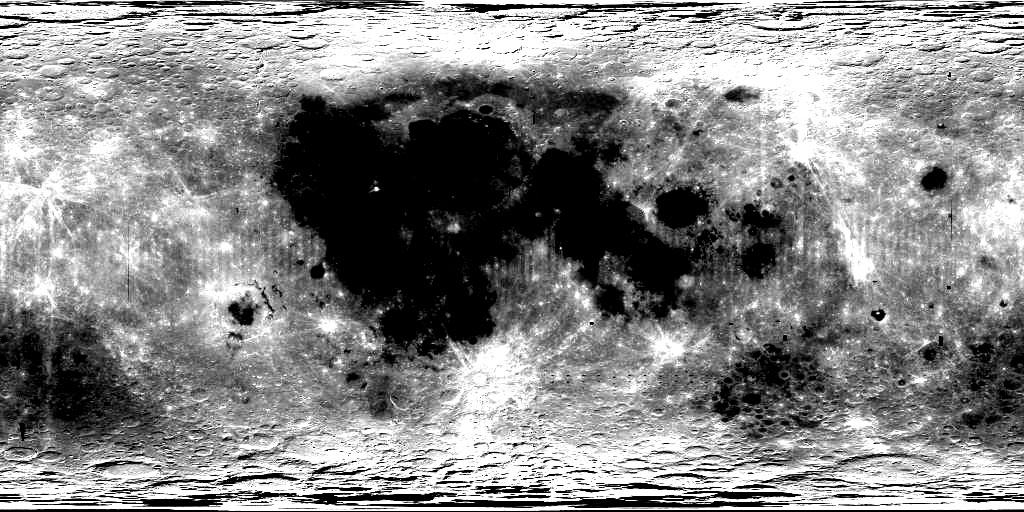
Unfortunately, several authors [Malin and Ravine, 1998; Cook et al., 2002a, 2002b] have noted that the image bore sights based on the (original mission) NAIF (JPL Navigation and Ancillary Information Facility) SPICE information have offsets of as much as 13 km (or more) from those based on revised SPICE derived from the CLCN solution. Comparing the original and revised SPICE information shows minor differences (0.6 km) in the images' spacecraft positions and major differences (8.0 km) in the pointing angles [Cook et al., 2002]. See Figure 2 for a global map showing the locations and magnitudes of the horizontal offsets. These offsets indicate errors in the original CLCN.
These offsets appear to have originated from a combination of factors, including: a) only a small number (22) of tie points were used to fix CLCN coordinates to ULCN coordinates (see Figure 1), b) the camera angles were unconstrained in the CLCN solution; and c) the tie points were unrealistically constrained to lie on a sphere of radius 1736.7 km. Efforts are underway to address these offsets (see Unified Lunar Control Network 2004).
Contact and Distribution
- Format
- Control Network
- Access Scope
- Astrogeology
- Native Data Set Environment
- Astrogeology Theme
- Geographic Information System (GIS)
- Mission Names
- Clementine
- Online Package Link
- https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/clementine_lunar_control_network
- External File Size
- 35854237
- Online File Link
- http://astropedia.astrogeology.usgs.gov/download/Moon/Research/ControlNetworks/zmea.dat
- Contact Address
- 2255 N. Gemini Drive
- Contact City
- Flagstaff
- Contact State
- AZ
- Contact Postal Code
- 86001
- Contact Email
- [email protected]
Geospatial Information
- Target
- Moon
- System
- Earth
- Object Type
- Grid Cell
- Quad Name
- Horizontal Coordinate System Units
- Degrees