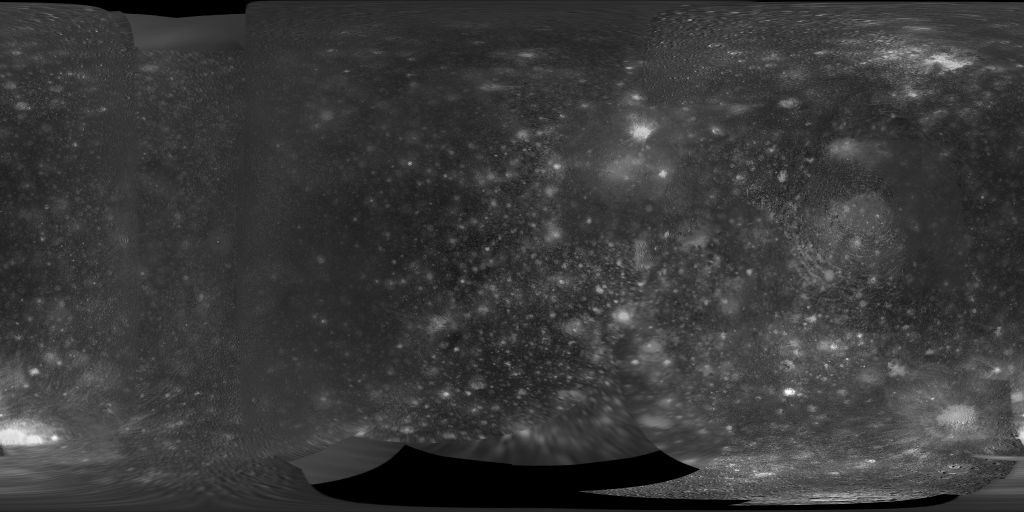
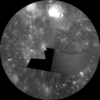
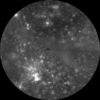
Callisto Galileo/Voyager Global Mosaic 1km
- Originators
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Publisher
- USGS Astrogeology Science Center
- Abstract
- This global map of Callisto utilizes the best image quality and moderate resolution coverage supplied by Galileo SSI (Solid State Imaging instrument) and Voyager 1 and 2. This mosaic was prepared using the ISIS 2 image processing and cartographic system and later converted to an ISIS 3 cube. The image data was selected on the basis of overall image quality, reasonable input resolution, and availability of moderate viewing and sun angles for topography. The average input resolution was 1.0 kilometers/pixel. The resolution ranged from 60 km/pixel for gap fill up to 400 meters/pixel.
- Purpose
- To build a global mosaic using the best available image data
Contact and Distribution
- Format
- Global Mosaic, Image, Raster Data, Remote-sensing Data
- Access Constraints
- public domain
- Access Scope
- Astropedia
- Use Constraints
- None
- Edition
- 1
- Supplemental Information
- http://geopubs.wr.usgs.gov/i-map/i2770/
- Native Data Set Environment
- ISIS v3
- Astrogeology Theme
- Geomorphology, Remote Sensing, Satellites
- Mission Names
- Galileo, Voyager
- Instrument Names
- SSI
- Online Package Link
- https://astrogeology.usgs.gov/search/map/callisto_galileo_voyager_global_mosaic_1km
- External File Size
- 110 MB
- Online File Link
- https://planetarymaps.usgs.gov/mosaic/Callisto_Voyager_GalileoSSI_global_mosaic_1km.tif
- Contact Address
- 2255 N. Gemini Drive
- Contact City
- Flagstaff
- Contact State
- AZ
- Contact Postal Code
- 86001
- Contact Email
- [email protected]
- Progress
- Complete
- Update Frequency
- As needed
- Logical Consistency
- The geometric control network was computed at the RAND Corporation using RANDâs most recent solution as of April 1999 (Davies and Katayama, 1981). This process involved selecting control points on the individual images, making pixel measurements of their locations, using reseau locations to correct for geometric distortions, and converting the measurements to millimeters in the focal plane. These data are combined with the camera focal lengths and navigation solutions as input to photogrammetric triangulation software that solves for the best-fit sphere, the coordinates of the control points, the three orientation angles of the camera at each exposure (right ascension, declination, and twist), and an angle (W0) which defines the orientation of Callisto in space. W0âin this solution 259.51°âis the angle along the equator to the east, between the 0° meridian and the equatorâs intersection with the celestial equator at the standard epoch J2000.0. This solution places the crater Saga at its defined longitude of 326° west (Seidelmann and others, 2002). * Davies, M.E., and Katayama, F.Y., 1981, Coordinates of features on the Galilean satellites: Journal of Geophysical Research, v. 86, no. A10, p. 8635â8657. * Seidelmann, P.K., Abalakin, V.K., Bursa, M., Davies, M.E., de Bergh, C., Lieske, J.H., Oberst, J., Simon, J.L., Standish, E.M., Stooke, P., and Thomas, P.C., 2002, Report of the IAU/IAG Working Group on Cartographic and Rotational Elements of the Planets and Satellitesâ2000: Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, v. 82, p. 83â110.
- Completeness Report
- The average input resolution was 1.0 kilometers/pixel. The resolution ranged from 60 km/pixel for gap fill up to 400 meters/pixel.
- Process Description
- This global map base uses the best image quality and moderate resolution coverage supplied by Galileo SSI and Voyager 1 and 2 (Batson, 1987; Becker and others, 1998; Becker and others, 1999; Becker and others, 2001). The digital map was produced using Integrated Software for Imagers and Spectrometers (ISIS) (Eliason, 1997; Gaddis and others, 1997). The individual images were radiometrically calibrated and photometrically normalized using a Lunar-Lambert function with empirically derived values (McEwen, 1991; Kirk and others, 2000). A linear correction based on the statistics of all overlapping areas was then applied to minimize image brightness variations. The image data were selected on the basis of overall image quality, reasonable original input resolution (from 20 km/pixel for gap fill to as much as 150 m/pixel), and availability of moderate emission/incidence angles for topography. Although consistency was achieved where possible, different filters were included for global image coverage as necessary: clear for Voyager 1 and 2; clear and green (559 nm) for Galileo SSI. Individual images were projected to a Sinusoidal Equal-Area projection at an image resolution of 1.0 kilometer/pixel. The final constructed Sinusoidal projection mosaic was then reprojected to the Mercator and Polar Stereographic projections included on this sheet. The final mosaic was enhanced using commercial software. * Batson, R.M., 1987, Digital cartography of the planetsâNew methods, its status, and its future: Photogrammetric Engineering and Remote Sensing, v. 53, no. 9, p. 1211â1218. * Gaddis, L.R., Anderson, J., Becker, K.J., Becker, T.L., Cook, D., Edwards, K., Eliason, E.M., Hare, T., Kieffer, H.H., Lee, E.M., Mathews, J., Soderblom, L.A., Sucharski, T., Torson, J., McEwen, A.S., Robinson, M.S., 1997, An overview of the Integrated Software for Imaging Spectrometers (ISIS), in Lunar and Planetary Science Conference XXVIII: Houston, Lunar and Planetary Institute, p. 387. * McEwen, A.S., 1991, Photometric functions for photoclinometry and other applications: Icarus, v. 92, p. 298â311. * Kirk, R.L., Thompson, K.T., Becker, T.L., and Lee, E.M., 2000, Photometric modeling for plane-tary cartography, in Lunar and Planetary Science Conference XXXI: Houston, Lunar and Planetary Institute, abs. no. 2025 [CD-ROM].
Geospatial Information
- Target
- Callisto
- System
- Jupiter
- Minimum Latitude
- -90
- Maximum Latitude
- 90
- Minimum Longitude
- 0
- Maximum Longitude
- 360
- Direct Spatial Reference Method
- Raster
- Object Type
- Grid Cell
- Raster Row Count (lines)
- 7569
- Raster Column Count (samples)
- 15138
- Bit Type (8, 16, 32)
- 8
- Quad Name
- Radius A
- 2409300.0488
- Radius C
- 2409300.0488
- Bands
- 1
- Pixel Resolution (meters/pixel)
- 1000.0051966711
- Scale (pixels/degree)
- 42.05
- Map Projection Name
- Simple Cylindrical
- Latitude Type
- Planetocentric
- Longitude Direction
- Positive West
- Longitude Domain
- 0 to 360