Level2 HiRISE¶
Prerequisites - HiRISE Level 1 Processed Images
- Up to 14 CCD images
- Imported into ISIS with
hi2isis spiceinitapplied to each- Radiometrically Calibrated with
hical - Noise Removed
- Imported into ISIS with
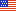
HiRISE Focal Plane Assembly - Illustration
Each CCD has 2048px in the cross scan direction. The 14 staggered CCDs overlap by 48px at each end. This gives a total width of ~20,000px for RED and 4,048px for the BG and IR images.
When the camera electronics read out the image data, each CCD is broken in two halves (left and right channels). On the ground, the data for one observation is up stored in 28 image files (14 CCDs with 2 channels each). A Level2 ISIS cube combines these CCD images into a single mosaic.
The Level2 process involves the following:
- Geometric transformation of each CCD image from spacecraft camera orientation to a common map coordinate system
- Correction of tonal mismatches among the projected images (optional)
- Creation of a HiRISE observation mosaic of the tone matched CCD images to create a complete HiRISE observation image.
The results of this process will be an uncontrolled observation mosaic, meaning that the output map will only be as accurate as the original SPICE allows. Software and procedures for creating controlled (adjusted SPICE) mosaics are underway. Information and documentation will be released on our site.
Map Projecting HiRISE Images¶
To assemble the HiRISE observation mosaic from the CCD images, use
cam2map
to convert each CCD image to a map projected image.
This example projects one image first, then uses the same projection for the others.
Alternatively, maptemplate
can create custom map files.
Part A: Project 1st image with cam2map
RED5 is a good choice to project first. It's near the center of the observation.
The output cube has the mapping parameters needed to project the other images, so they can be mosaicked.
The default projection for cam2map is sinusoidal,
so the resulting RED5 image is now in sinusoidal projection.
Part B: Project the rest of the images with cam2map
cam2map from=PSP_002733_1880_?.norm.cub \
to=PSP_002733_1880_?.sinu.cub \
map=PSP_002733_1880_RED5.sinu.cub pixres=map
The RED5 sinusoidal cube is used as the map file. The remaining CCD images will use the same projection parameters as RED5. When mosaicking, all input images for the mosaic must have the same projection parameters.
-
Creates a map file that can be used to project images
-
Geometrically transforms a raw camera image to a map projected image
Tone Matching¶
Tone-match images with equalizer
-
Hold the tone of the RED5 CCD image.
The pixel values in RED5 won't be changed. RED0-4 and RED6-9 will be normalized to RED5's tone. Make a list the filename(s) that will be held. -
List all images to be normalized.
Their contrast/brightness will be updated so that tones match the RED5 image on the hold list. This will normalize to the RED calibration.equalizeranalyzes the pixels in the overlap regions to calculate its corrections.
-
Run
equalizerwith the two lists created above as input.
The output should be ten cubes (RED0-9) with .equ.cub extension.
Mosaicking¶
Constructing a Mosaic with automos
A new list of the equalized cube filenames is required as input.
Only add filenames for one observation (or adjacent observations) to the list file, otherwise all the images in the list will be mosaicked into a single output image.
The example created a mosaic with RED images.
Near-infrared (IR) and blue-green (BG) images follow a similar process.